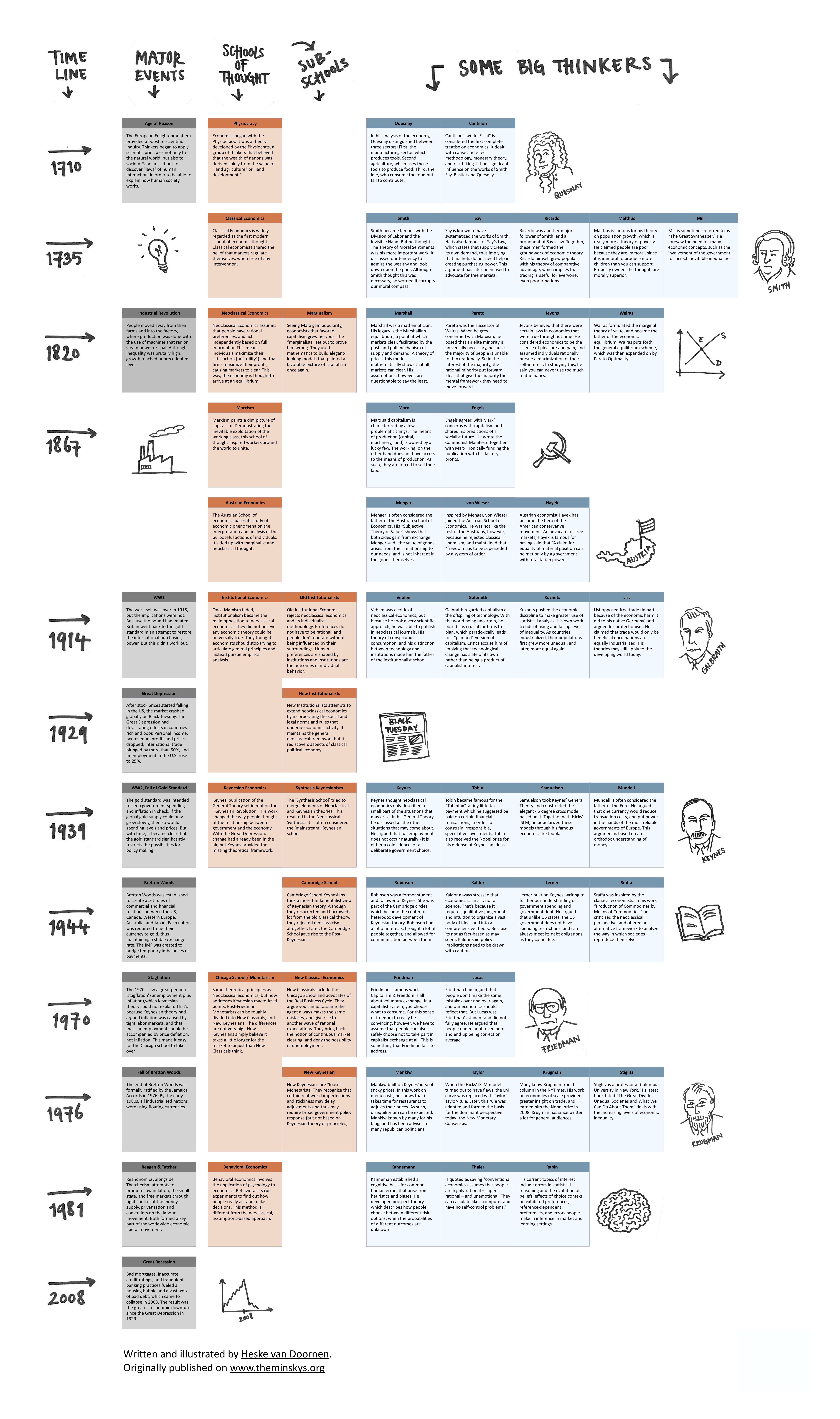
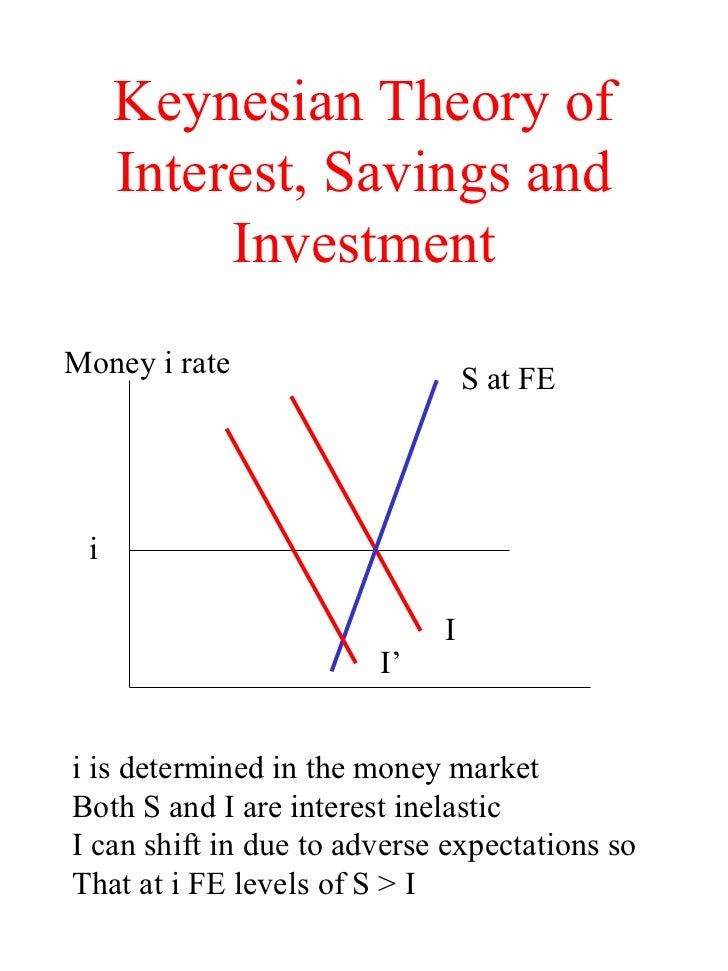
The Theory Of Keynesian Economics

Keynes's grandmother wrote to him saying that, since he was born in Cambridge, people will expect him to be clever. John Maynard Keynes was born in CambridgeCambridgeshireEnglandto an upper-middle-class https://modernalternativemama.com/wp-content/custom/research-paper/babylon-revisited-summary.php. His father, John Neville Keyneswas an economist and a lecturer in moral sciences at the University of Cambridge and his mother Florence Ada Keynes a local social reformer.
Keynes was the first born, and was followed by two more children — Margaret Neville Keynes in and Geoffrey Keynes in Geoffrey became a surgeon and Margaret married the Nobel Prize-winning physiologist Archibald Hillalthough she had many affairs with women, notably Eglantyne Jebb. They remained in the same house throughout their lives, where the children were always welcome to return.
Navigation menu
Keynes would receive considerable support from his father, including expert coaching to help him pass his scholarship exams and financial help both as a young man and when his assets were nearly wiped out at the onset of Great Depression in Keynes's mother made her children's interests her own, and according to Skidelsky, "because she could grow up with her children, they never outgrew home". He quickly showed a talent for arithmetic, but his health was poor leading to several long absences. He was tutored at home by a governess, Beatrice Mackintosh, and his mother. In Januaryat eight and a half, he The Theory Of Keynesian Economics as a day pupil at St Faith's preparatory school. ByKeynes was top of his class and excelling at mathematics.
The Keynesian Theory
InSt Faith's headmaster, Ralph Goodchild, wrote that Keynes was "head and shoulders above all the other boys in the school" and was confident that Keynes could get a scholarship to Eton. In Keynes left Eton for King's College, Cambridgeafter receiving a scholarship for this also to read mathematics.
Alfred Marshall begged Keynes to become an economist, [18] although Keynes's own inclinations drew him towards philosophy — especially The Theory Of Keynesian Economics ethical system of G. Keynes was elected to the University Pitt Club [19] and was an active member of the semi-secretive Cambridge Apostles society, a debating club largely reserved for the brightest students. Like many members, Keynes retained a bond to the club after graduating and continued to attend occasional meetings throughout his life. He was said to be an atheist.
Aside from The Theory Of Keynesian Economics few months spent on holidays with family and friends, Keynes continued to involve himself with the university over the next two years. He took part in debates, further studied philosophy and attended economics lectures informally as a graduate student for one term, which constituted his only formal education in the subject.
He took civil service exams in The economist Harry Johnson wrote that the optimism imparted by Keynes's early life is a key to understanding his later thinking. According to Skidelskythe sense of cultural unity current in Britain from the 19th century to the end of World War I provided a framework with which the well-educated could set various spheres of knowledge in relation to each other and life, enabling them to confidently draw from different fields when addressing practical problems.
By Keynes had published his first professional economics article in The Economic Journal source, about the effect of a recent global economic downturn on India.
Also inKeynes accepted a lectureship in economics funded personally by Alfred Marshall. Keynes's earnings rose further as he began to take on pupils for private tuition. In Keynes was made the editor of The Economic Journal.
By he had published his first book, Indian Currency and Finance. His written work was published under the name "J M Keynes", though to his family and friends he was known as Maynard. His father, John Neville Keynes, was also always known by his middle name. While he did not formally re-join the civil service inKeynes traveled to London at the government's request a few days before hostilities started. Bankers had been pushing for the suspension of specie payments — the convertibility of banknotes into gold — but with Keynes's help the Chancellor of the Exchequer then Lloyd George was persuaded The Theory Of Keynesian Economics this would be a bad idea, as it would hurt the future reputation of the city if payments were suspended before it was necessary.
In January The Theory Of Keynesian Economics took up an official government position at the Treasury. Among his responsibilities were the design of terms of credit between Britain and its continental allies during the war and the acquisition of scarce currencies.]
Opinion: The Theory Of Keynesian Economics
| THE UNTRANSLATABLE WORD MACHO ANALYSIS | 475 |
| CASE STUDY D2 | 143 |
| The Theory Of Keynesian Economics | 66 |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Theory Of Keynesian Economics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit3keynesianismvsmonetarism-140525124425-phpapp01/95/keynesianism-vs-monetarism-7-638.jpg?cb=1401021946)
The Theory Of Keynesian Economics Video
What is The Keynesian Theory?

Category
Best Posts
- Effects And Statistics Of Gambling
- The Different Perspectives Of Success In Outliers
- professional editing services
- Causes Of Low Self Esteem
- Sex Trafficking The Second Largest Illegal Industry
- Baseball and Its History
- professional writing editing services
- Why Does Socrates Think That Right Conduct
- Helen Keller: The Story Of My Life
- buying essays
- favorite quotation st augustine
- Dividend Policy





 647
647