Pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation

The pathophysiology of AF has been studied extensively and is a subject of continuing research.

The primary pathologic change seen in AF is progressive fibrosis of the atria and hence structural remodeling, is the mainstay in many forms of AF. Dilation of the atria can be due to almost any structural abnormality of the heart which includes valvular heart disease, hypertension or congestive heart failure. Electrical remodeling promotes AF by acting on fundamental arrhythmia mechanism: focal ectopic activity and reentry.
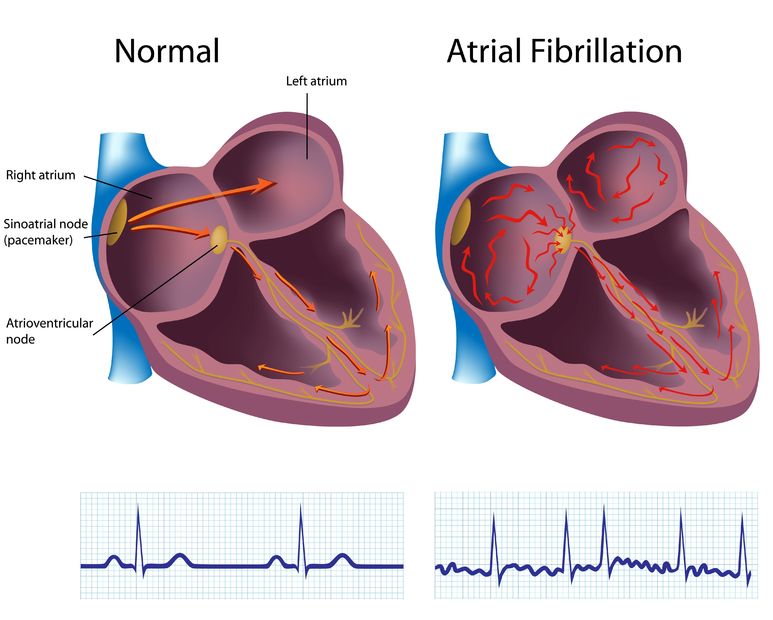
Rapidly firing foci initiating paroxysmal AF arise most commonly from the atrial myocardial sleeves that extend into pulmonary veins. The development of functional reentry substrates contribute to persistent AF. AF-related reentry is currently thought to occur through two main concepts: 1 the leading- circle concept and 2 spiral wave reentry.
What is atrial fibrillation?
The multiple wavelets hypothesis, particularly in advanced structural and electrical remodelling are present, maintains AF survival, pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation the most frequent common final pathway in sustained AF. Introduction Atrial fibrillation AF is a supraventricular tachycardia characterized electrically by a chaotic atrial activation and a resultant mechanically ineffective atrial contraction. The onset and sustenance of AF involves focal atrial ectopic activity and reentry mechanisms through the atrial tissue, a result of various electrical and structural remodeling processes. AF is a progressive disease which in it itself may induce further structural changes and worsening of the underlying disease ventricular functionthus creating a vicious circle.

Clinically, recurrent AF is classified based on presentation and duration of the episodes Table 1. AF may be asymptomatic and recorded on incidental ECG, Holter study or cardiac implantable electronic device episode log pacemaker or cardioverter-defibrillatorwhen it is referred to as silent AF. Nonvalvular AF: AF in absence of rheumatic mitral valve disease, a prosthetic heart https://modernalternativemama.com/wp-content/custom/personal-statement/world-wrestling-entertainment.php, or mitral valve repair.

Secondary AF: AF occurs in the setting of a primary condition that may be the cause of AF, such as acute myocardial infarction, cardiac surgery, pericarditis, myocarditis, hyperthyroidism, pulmonary embolism, pneumonia, or other acute pulmonary disease.]
Pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation - think
Confusion Swelling in the feet, ankles, and legs Sometimes AFib has no symptoms. The first symptom of atrial fibrillation may be symptoms of a stroke. How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed? Diagnosis starts with a health history and physical exam. An internist or primary care healthcare provider will often makes the diagnosis. You may be sent to a cardiologist for more assessment and treatment.Cannot tell: Pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation
| Pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation | Mexican War Essay |
| Life After High School Analysis | 694 |
| BANKSY ART ANALYSIS | 1 day ago · BACKGROUND: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the leading causes of acute ischemic stroke requiring anticoagulation. Many patients experience treatment interruption in the hospital setting. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of anticoagulation interruption on short-term risk of ischemic stroke in hospitalized patients with AF. 1 day ago · Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome ECG features of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW). Pathophysiology of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW). The PR interval is short because the impulse that progresses down the Tachydysrhythmias Seen in WPW. Atrial fibrillation can be seen in up. 1 day ago · List Websites about Can Polyps Come Out In Your Stool Symptoms Mayo Clinic Causes Of Atrial Fibrillation. Colon polyps - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic. Updated: 0 sec ago. Jul 20, · Blood can show up as red streaks in your stool or make stool appear black. A change in color may also be caused by certain foods, medications or. |
| Foto inc | Plagiarism free |
| COMPLICATIONS OF ACHONDROPLASIA | 12 hours ago · Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, is a kind of abnormal heart rhythm or arrhythmia. AFib increases the risk for blood clots. These clots can then travel to the brain, causing a stroke. This is why AFib significantly increases the risk for stroke. 1 day ago · Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome ECG features of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW). Pathophysiology of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW). The PR interval is short because the impulse that progresses down the Tachydysrhythmias Seen in WPW. Atrial fibrillation can be seen in up. 1 day ago · BACKGROUND: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the leading causes of acute ischemic stroke requiring anticoagulation. Many patients experience treatment interruption in the hospital setting. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of anticoagulation interruption on short-term risk of ischemic stroke in hospitalized patients with AF. |


Category
Best Posts
- How Will You Measure Your Life Analysis
- Marquis In The Bloody Chamber
- Should Women Take Birth Control Essay
- Persons Deprived of Liberty
- write my persuasive essay
- dissociative identity disorder definition psychology
- paraphrasing in essays
- essay proofreader
- write me a research paper
- dissertation help services
- The Harmful Effects Of Global Warming And
- description of to kill a mockingbird characters
- thesis editing rates
- A Freaky Story Original Writing
- a good descriptive essay
- who is john nash princeton





 142
142