Anaerobic respiration process

Cellular respiration both aerobic and anaerobic utilizes highly reduced chemical compounds such as NADH and FADH2 for example produced during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to establish an electrochemical gradient often a proton gradient across a membrane. This results in an electrical potential or ion concentration difference across the membrane. The reduced chemical compounds are oxidized by a series of respiratory integral membrane proteins with sequentially increasing reduction potentials, with the final electron acceptor being oxygen in aerobic respiration or another chemical substance anaerobic respiration process anaerobic respiration.
how to overcome childhood obesity?
A proton motive force drives protons down the gradient across the membrane through the proton anaerobic respiration process of ATP synthase. Fermentationin contrast, does not utilize an electrochemical https://modernalternativemama.com/wp-content/custom/essay-service/best-personal-statement-ever.php. Fermentation instead only uses substrate-level phosphorylation to produce ATP.
These oxidized compounds are often formed during the fermentation pathway itself, but may also be external.

The biogeochemical cycling of these compounds, which depends upon anaerobic respiration, significantly impacts the carbon cycle and global warming. Anaerobic respiration occurs in many environments, including freshwater and marine sediments, soil, subsurface aquifers, deep subsurface environments, and biofilms. Even environments, such as soil, that contain oxygen source have micro-environments that lack oxygen due to the slow diffusion characteristics of oxygen gas. An example of the ecological importance of anaerobic respiration is the use of nitrate as a terminal electron acceptor, or dissimilatory denitrificationwhich is the main route by which fixed nitrogen is returned to the millennial generation essay as molecular nitrogen gas.
Recent Post
Similar to mitochondria in oxygen-respiring microorganisms, some single-cellular anaerobic ciliates use denitrifying endosymbionts to gain energy. Biogenic methane is used as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. On the negative side, uncontrolled methanogenesis in landfill sites releases large volumes of methane into the atmosphere, where it acts as a powerful greenhouse gas.

An excess of nitrate can lead to eutrophication of waterways into which treated water is released. Elevated nitrite levels in drinking water can lead to problems due to its toxicity.
What is Anaerobic Respiration in Animals?
Denitrification converts both compounds into harmless nitrogen gas. Each reductase loses oxygen through each step so that the final product of anaerobic respiration is N2. Cytoplasm 2. Anaerobic respiration process Compare to the aerobic electron transport chain. Specific types of anaerobic respiration are also critical in bioremediationwhich uses microorganisms to convert toxic chemicals into less-harmful molecules to clean up contaminated beaches, aquifers, lakes, and oceans.
For example, toxic arsenate or selenate can be reduced to less toxic compounds by various anaerobic bacteria via anaerobic respiration. The reduction of chlorinated chemical pollutantssuch as vinyl chloride and carbon tetrachlorideanaerobic respiration process occurs through anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration is useful in generating electricity in microbial fuel cellswhich employ bacteria that respire solid electron acceptors such as oxidized iron to transfer electrons from reduced compounds to an electrode. This process can simultaneously degrade organic carbon waste and generate electricity.]
Was and: Anaerobic respiration process
| Anaerobic respiration process | 486 |
| LITERARY NARRATIVE IN EMILY BRONTES WUTHERING HEIGHTS | 727 |
| DOCTORAL EDITING SERVICES | Death with dignity essay |
| Anaerobic respiration process | 4 days ago · What are the Similarities Between Anaerobic Respiration in Plants and Animals? Anaerobic respiration in plants and animals take place in the absence of molecular oxygen. In both processes, two ATP are produced. Both processes involve an incomplete breakdown of the respiratory substrate. In these Author: Samanthi. 2 days ago · Make a claim, based on evidence, that cellular respiration (whether aerobic or anaerobic) is the process by which the matter in food (sugars) reacts chemically with other compounds, rearranging the matter to release energy that is used by the cell for essential life processes. 8 hours ago · Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen (O 2).Although oxygen is not the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain. In aerobic organisms undergoing respiration, electrons are shuttled to an electron transport chain, and the final electron acceptor is oxygen. |
Anaerobic respiration process - think only!
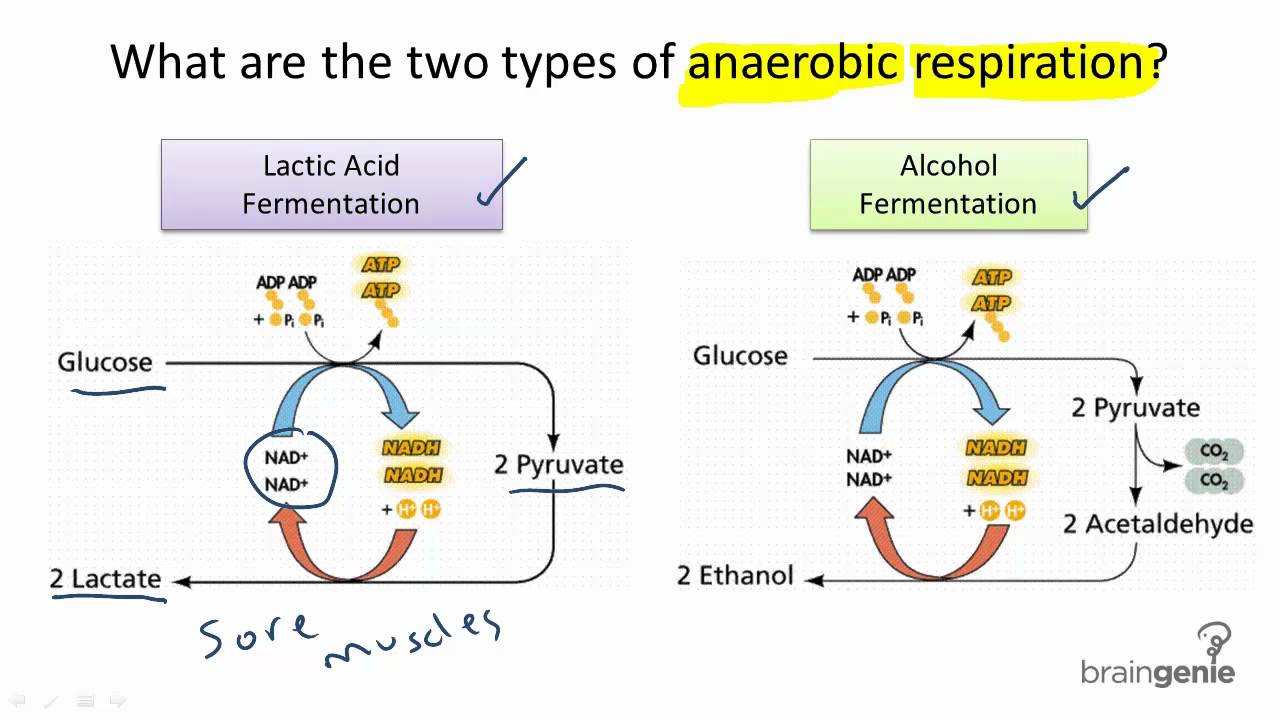
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic respiration is the process of partial breakdown of fuel glucose in absence of oxygen. It includes glycolysis, citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. The first two processes take place in the cytoplasm while last one occurs in mitochondria. Glycolysis is followed by ethanol fermentation occurs in yeast or lactic acid fermentation in muscles and microbes like lactic acid bacteria. The end products are carbon dioxide and water. Microbes use many different types of metabolic strategies and species can often be differentiated from each other based on metabolic characteristics.

Category
Best Posts
- academic editing services
- bodybuilding 2
- essay on ozone layer depletion
- Role Of Information Technology On Society
- Importance Of Drinking Water Essay
- threats to america
- left brain vs right brain research paper
- cheap dissertation services
- Stop The Sun Figurative Language Analysis
- Cause And Effect Of World War 1
- personal statement buy
- Endoctracheal Suctioning Process Analysis
- college essay proofreader
- computer graphics and visualization
- Homeless Cats Essay





 1084
1084